Like many other common WordPress errors, the 403 Forbidden error is an HTTP status code that a web server uses to communicate with your web browser.
Quick background on HTTP status codes – whenever you connect to a website with your browser, the web server responds with something called an HTTP header. Usually, this all happens behind the scenes because everything is working normally (that’s a 200 status code, in case you were wondering).
However, if something goes wrong, the server will respond back with a different numbered HTTP status code. While these numbers are frustrating to encounter, they’re actually quite important because they help you diagnose exactly what’s going wrong on your site.
The 403 Forbidden error means that your web server understands the request that the client (i.e. your browser) is making, but the server will not fulfill it.
In more human-friendly terms, it basically means that your server knows exactly what you want to do, it just won’t let you do it because you don’t have the proper permissions for some reason. It’s kind of like you’re trying to get into a private event, but your name got accidentally removed from the guest list for some reason.
Other HTTP status codes mean different things. We’ve written guides on fixing issues with 404 not found errors, 500 internal server errors, 502 bad gateway errors, and 504 gateway timeout errors.
What Causes the 403 Forbidden Error on WordPress?
The two most likely causes of the 403 Forbidden Error on WordPress are:
- Corrupt
.htaccess file
- Incorrect file permissions
It’s also possible that you’re seeing the error because of an issue with a plugin that you’re using at your site. In this article, we’ll show you how to troubleshoot all of these potential issues.
403 Forbidden Error Variations
Like many other HTTP status codes, there are a lot of different variations for how this error code presents itself.
Here are some common variations that you might come across:
- “Forbidden – You don’t have permission to access / on this server”
- “403 – Forbidden: Access is denied”
- “Error 403 – Forbidden”
- “403 – Forbidden Error – You are not allowed to access this address”
- “403 Forbidden – nginx”
- “HTTP Error 403 – Forbidden – You do not have permission to access the document or program you requested”
- “403 Forbidden – Access to this resource on the server is denied”
- “403. That’s an error. Your client does not have permission to get URL / from this server”
- “You are not authorized to view this page”
Basically, if you see any mention of “forbidden” or “not allowed to access”, you’re probably dealing with a 403 Forbidden error.
How to Fix 403 Forbidden Error on WordPress
To help you fix the 403 Forbidden Error on your WordPress site, we’ll cover three separate troubleshooting steps in detail:
- File permissions
- .htaccess file
- Plugin issues
Potential Fix #1: File Permissions
Each folder and file on your WordPress site’s server has its own unique file permissions that control who can:
- Read – see the data in the file/view the contents of a folder.
- Write – modify the file/add or delete files inside a folder
- Execute – run the file and/or execute it as a script/access a folder and perform functions and commands.
These permissions are indicated by a 3-digit number, with each digit indicating the level of permission for each of the 3 categories above.
Normally, these permissions just “work” for your WordPress site. However, if something gets messed up with the file permissions at your WordPress site, it can cause the 403 Forbidden error.
To view and modify your site’s file permissions, you’ll need to connect via FTP/SFTP. Here’s how to use SFTP if you’re hosting at Host SEO.
For the screenshots in the tutorial below, we’ll be using the free FileZilla FTP program. The basic principles will apply to any FTP program, though – you’ll just need to apply them to a different interface.
Once you’re connected to your server, you can view a file or folder’s permissions by right-clicking on it:
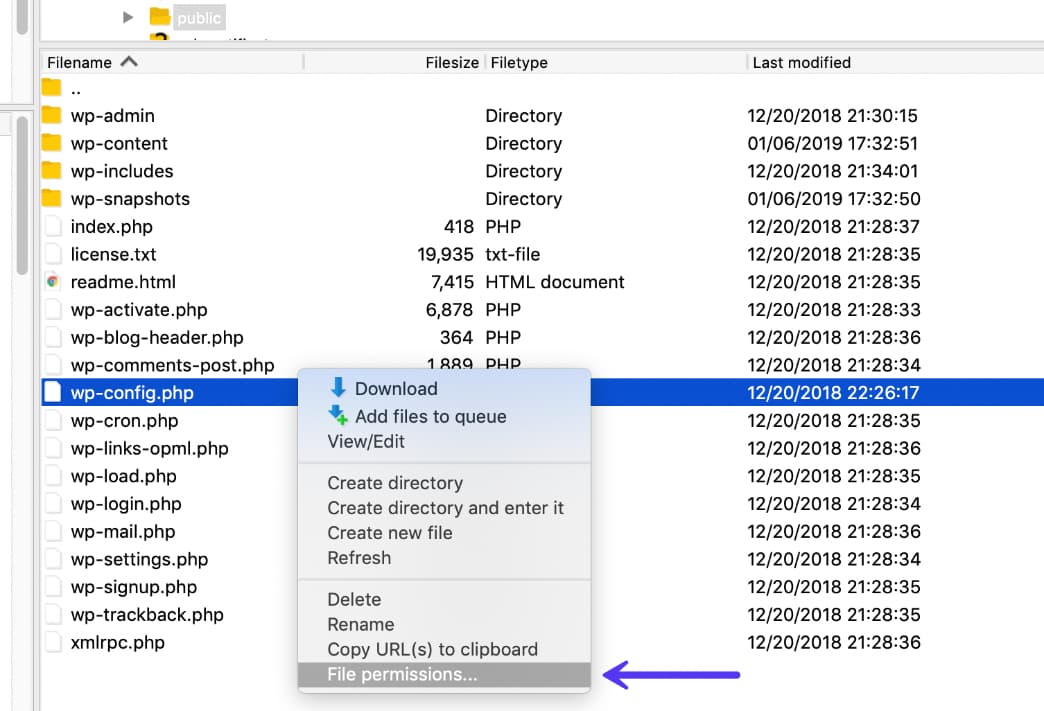
Of course, manually checking the permissions for each file or folder isn’t really an option. Instead, you can automatically apply file permissions to all the files or folders inside of a folder.
According to the WordPress Codex, the ideal file permissions for WordPress are:
- Files – 644 or 640
- Directories – 755 or 750
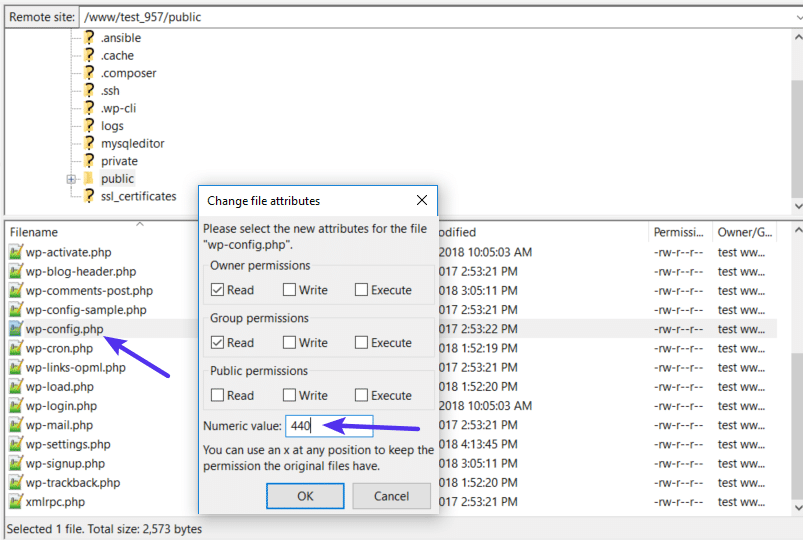
One exception is that your wp-config.php file should be 440 or 400.
To set these permissions, right-click on the folder that contains your WordPress site (the folder name is public at Host SEO). Then, choose File Attributes:
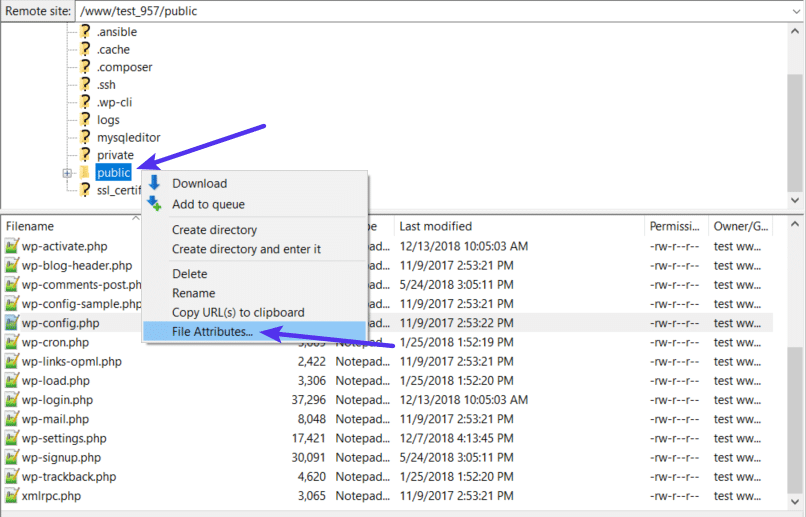
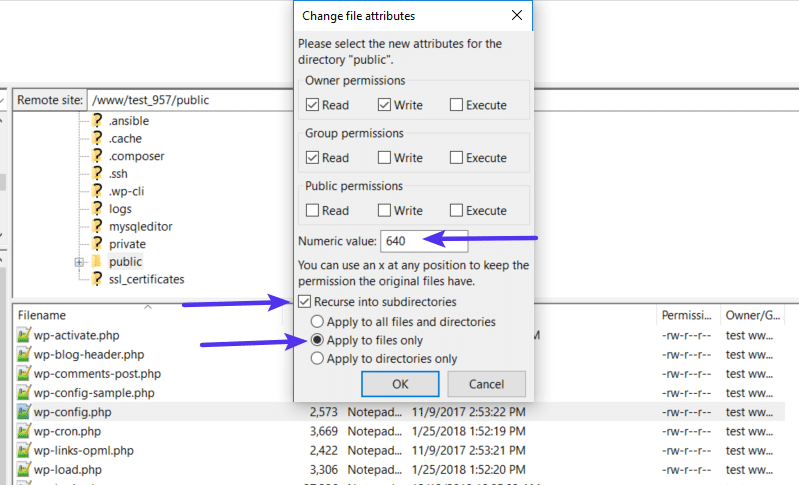
Enter 755 or 750 in the Numeric value box. Then, choose Recurse into subdirectories and Apply to directories only:
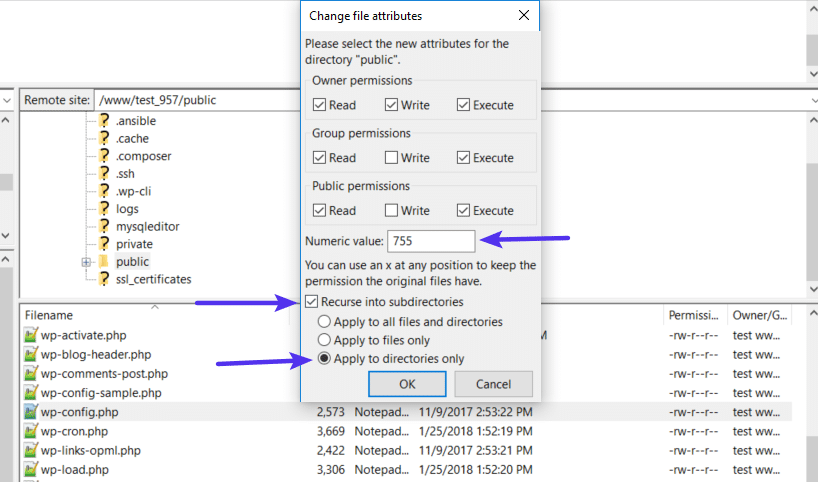
Once you’ve applied the correct permissions for directories, you’ll repeat the process for files. Only this time:
- Enter 644 or 640 in the Numeric value box
- Choose Recurse into subdirectories
- Choose Apply to files only
To finish the process, you just need to manually adjust the permissions for your wp-config.php file to make them 440 or 400:
If file permissions issues were causing the 403 Forbidden Error, your site should now start working again.
Potential Fix #2: .htaccess File
Host SEO uses the NGINX web server, so this potential issue doesn’t apply if you’re hosting your site at Host SEO because Host SEO sites do not have a .htaccess file.
However, if you’re hosting elsewhere and your host uses the Apache web server, one common cause of the 403 Forbidden error is a problem in your site’s .htaccess file.
The .htaccess file is a basic configuration file used by the Apache web server. You can use it to set up redirects, restrict access to all or some of your site, etc.
Because it’s so powerful, even if a little mistake can cause a big issue, like the 403 Forbidden error.
Rather than trying to troubleshoot the .htaccess file itself, a simpler solution is to just force WordPress to generate a new, clean .htaccess file.
To do that:
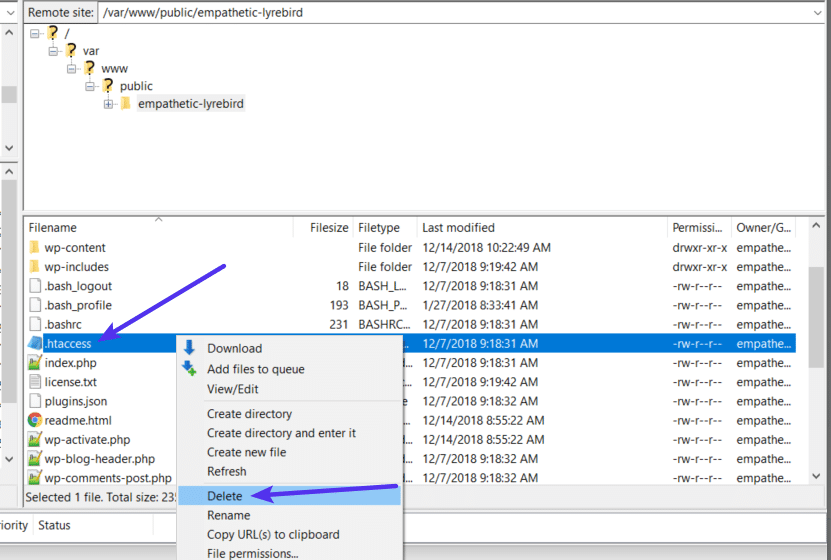
- Connect to your server via FTP
- Find the
.htaccess file in your root folder
- Download a copy of the file to your computer (it’s always a good idea to have a backup just in case)
- Delete the
.htaccess file from your server after you have a safe backup copy on your local computer
Now, you should be able to access your WordPress site if your .htaccess file was the issue.
To force WordPress to generate a new, clean .htaccess file:
- Go to Settings → Permalinks in your WordPress dashboard
- Click Save Changes at the bottom of the page (you do not need to make any changes – just click the button)
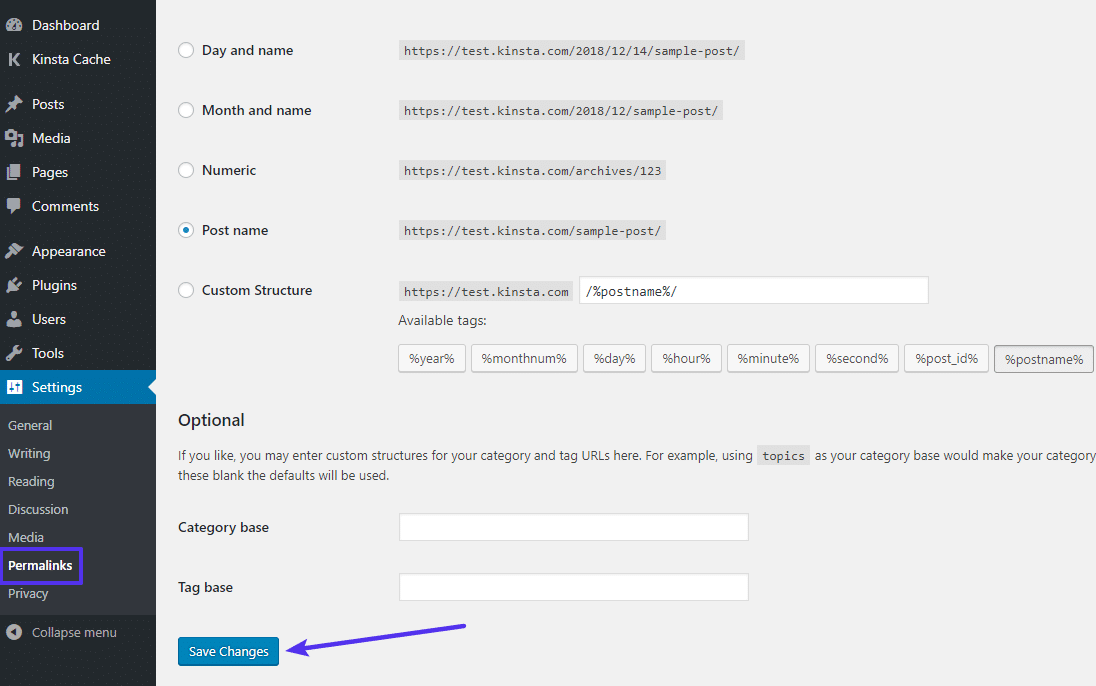
And that’s it – WordPress will now generate a new .htaccess file for you.
Potential Fix #3: Deactivate and then Reactivate Your Plugins
If neither your site’s file permissions nor .htaccess file are the problems, the next place to look is your plugins. It could be a bug in a plugin or a compatibility issue between different plugins.
No matter what the issue is, the easiest way to find the problematic plugin is with a little trial and error. Specifically, you’ll need to deactivate all of your plugins and then reactivate them one by one until you find the culprit.
If you can still access your WordPress dashboard, you can perform this process from the normal Plugins area.
If you cannot access your WordPress dashboard, you’ll instead need to connect to your WordPress site’s server via FTP/SFTP (here’s how to connect via SFTP at Host SEO).
Once you’re connected to your server via FTP:
- Browse to the wp-content folder
- Find the plugins folder inside of the wp-content folder
- Right-click on the plugins folder and choose Rename
- Change the name of the folder. You can name it anything different, but we recommend something like plugins-disabled to make it easy to remember.
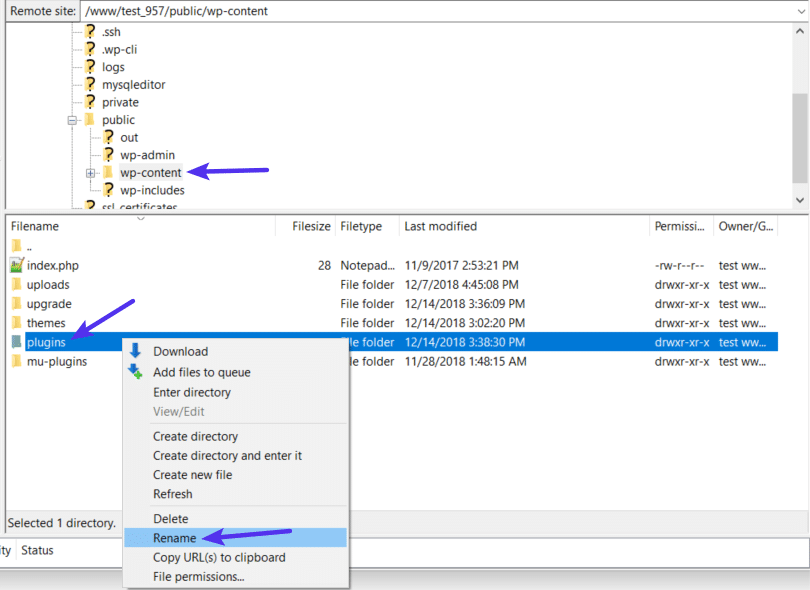
By renaming the folder, you’ve effectively disabled all the plugins at your site.
Now, try accessing your site again. If your site is working, you know that one of your plugins is causing the 403 Forbidden error.
To find the culprit, reactivate your plugins one-by-one until you find which plugin is causing the issue.
After changing the file name of the plugins folder, you should see a number of errors that say plugin file does not exist when you go to the Plugins area on your site:
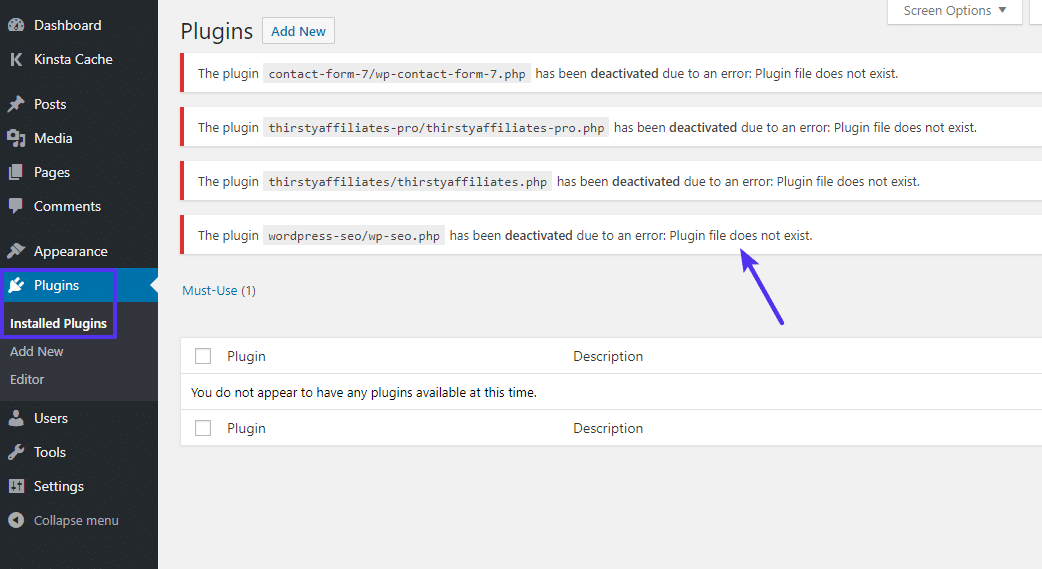
To fix this issue and regain the ability to manage your plugins, use your FTP program to change the name of the folder back to plugins. So, if you renamed it to plugins-disabled, just change it back to plugins.
Once you do that, you’ll see the full list of all your plugins again. Only now, they’ll all be deactivated:
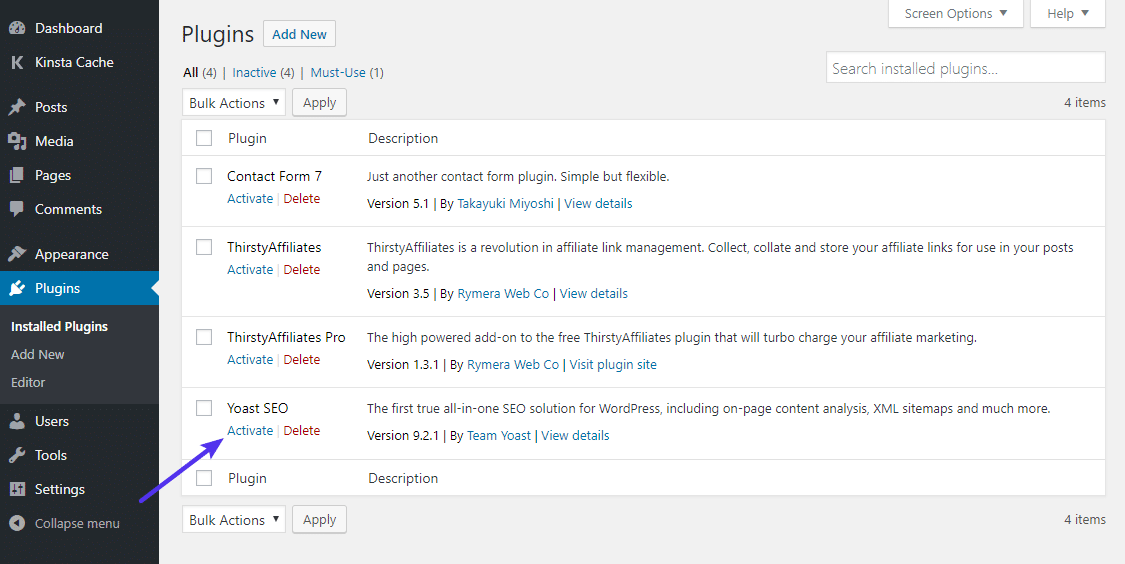
Use the Activate button to reactivate them one-by-one.
Once you find the plugin that’s causing the issue, you can either reach out to the plugin’s developer for help or choose an alternate plugin that accomplishes the same thing (we’ve collected the best WordPress plugins here).
Summary
The 403 Forbidden error means that your server is working, but you no longer have permission to view all or some of your site for some reason.
The two most likely causes of this error are issues with your WordPress site’s file permissions or .htaccess file. Beyond that, some plugin issues might also cause the 403 Forbidden error.
By following the troubleshooting steps in this guide, you should be able to get your site back to working in no time.