DRBD – Heartbeat ( Active/Passive High Availability Cluster )
- Category : Linux Helpline (Easy Guide)
- Posted on : Jun 16, 2019
- Views : 2,928
- By : Zane P.
Overview:
DRBD – Heartbeat cluster a good Active / Passive cluster solution for small scale applications using two servers in active and passive mode. This means , only one server will work at a time while keeping the other server as a backup with realtime data updates. DRBD is a kernel level service which will replicate your block devices ( HDD partition ) with the second server. So all the data that required for working your application must be need to place in that hard disk partition. Also make sure that both of your servers need same amount of free space.
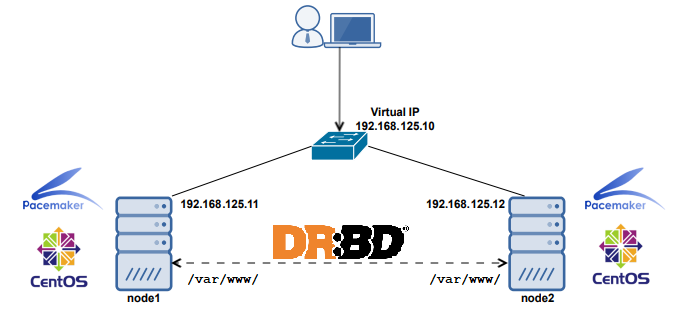
Heartbeat is a service which will manage the IP high availability and other services in your servers. You can also integrate CRM along with heartbeat for your big cluster projects. Please see the pictorial representation of this cluster below.
HA IP: 10.0.0.100 -> This will be the high availability IP. Your website/application may need to point to this IP. This IP will be available only in the Active server . If the active server go down it will be switched to Passive server
Active Server : 10.0.0.101 -> This is your active server
Passive Server : 10.0.0.102 -> This will be your passive server , means backup server.
In both active and passive server we need a hard disk partition , let us say /dev/sdb1 with equal amount of disk space. The DRDB service will synchronize the hdd partitions via a drdb block file called /dev/drbd0. So keep in mind that this drdb block files is always refers to your original disk partition. So we are going to build this Active passive services with high availability.
Software Requirements:
You may need Centos 5.x or later version , because Centos already have drbd and heartbeat as binary distributions, otherwise you need to compile and install drbd and heartbeat from source.
Pre configuration:
You may need to disable SELinux your server and remove iptable firewalls. Also you need to edit /etc/hosts file in your active and passive servers as follows and make sure it is pointing to correct IPs.
10.0.0.101 active.yourserver.com 10.0.0.102 passice.yourserver.com
Now you need to unmount your disk partition /dev/sdb1 and remove it from /etc/fstab too. We will erase this partition in the coming sessions. Also create a folder called /data, which we will use as mount point of drbd devic.
DRDB installation:
Let us install drbd first . You may need to install it in both servers and the drdb configuration must be unique.
# yum -y install kmod-drbd drbd
Now Edit /etc/drbd.conf as follows,
resource mydrdb {
protocol C;
handlers {
pri-on-incon-degr “echo ‘DRBD: primary requested but inconsistent!’ | wall; /etc/init.d/heartbeat stop”; #”halt -f”;
pri-lost-after-sb “echo ‘DRBD: primary requested but lost!’| wall; /etc/init.d/heartbeat stop”; #”halt -f”;
}
startup {
degr-wfc-timeout 30; # 30 seconds
}
disk {
on-io-error detach;
}
net {
timeout 120;
connect-int 20;
ping-int 20;
max-buffers 2048;
max-epoch-size 2048;
ko-count 30;
cram-hmac-alg “sha1″;
shared-secret “drdbTest1gKey”;
}
syncer {
rate 50M; # synchronization data transfer rate
al-extents 257;
}
on active.yourserver.com {
device /dev/drbd0;
disk /dev/sdb1;
address 10.0.0.101:7789;
meta-disk internal;
}
on passive.yourserver.com {
device /dev/drbd0;
disk /dev/sdb1;
address 10.0.0.102:7789;
meta-disk internal;
}
}
Hope you already umounted the partition /dev/sdb1 . Let us make it clear using the following command
# dd if=/dev/zero of= /dev/sdb1 bs=1M count=50
Now create the DRDB partition as follows,
# drbdadm create-md mydrbd
Format the drbd partition /dev/drbd0 with label mydrdb
# mkfs.ext3 -L mydrdb /dev/drbd0
Now let us start DRDB in both servers as follows,
# /etc/init.d/drbd start
Now login to your active server and do the following command , this command will tell the DRDB that current server is primary
# drbdadm – primary mydrbd
Now you can check the status of drdb either from /proc/drdb or using the command etc/init.d/drbd status. You can see the DRDB started syncing in /proc/drdb
If it is not working, there will be some issues in your installation procedure. If all ok let us proceed with the next step.
Heartbeat Installation:
You can use yum itself to install heartbeat
# yum -y install heartbeat heartbeat-pils heartbeat-stonith
There are 3 main configuration files and one resource script folders for heartbeat as follows,
/etc/ha.d/ha.cf -> The heartbeat configuration file
/etc/ha.d/haresources -> The hearbeat resource file , in which we specify high availability IP and services lists which need to start automatically by heartbeat
/etc/ha.d/authkeys -> Hearbeat servers authentication keys.
/etc/ha.d/resource.d/ -> This contain a set of init scripts which we use in “haresource” file for managing services
First let us create the heartbeat configuration file , /etc/ha.d/ha.cf , as follows,
# Heartbeat logging configuration logfacility daemon
# Heartbeat cluster members node active.yourserver.com node passive.yourserver.com
# Heartbeat communication timing keepalive 1 warntime 10 deadtime 30 initdead 120
# Heartbeat communication paths udpport 694 ucast eth0 10.0.0.101 # make sure this ips are on eth0 ucast eth0 10.0.0.102 baud 19200
# fail back automatically auto_failback on
# Monitoring of network connection to default gateway ping 10.0.0.1 # ping to gate way for network testing respawn hacluster /usr/lib/heartbeat/ipfail
Now let us create an haresource file as follows,
active.yourserver.com IPaddr::10.0.0.100/24 drbddisk::mydrdb Filesystem::/dev/drbd0::/data::ext3 mysqld httpd
Let me explain the above terms,
The first term active.yourserver.com means all the following services must be available in active server, if that server is available.
IPaddr::10.0.0.100/24 -> This term will call the init script /etc/ha.d/resource.d/IPaddr and activate the HA IP 10.0.0.100
drbddisk::mydrdb -> This term will call the init script /etc/ha.d/resource.d/drbddisk and make the switching to primary or seconday to drdb disk labeled mydrdb
Filesystem::/dev/drbd0::/data::ext3 -> This term will call the init script /etc/ha.d/resource.d/Filesystem and which will mount the drdb disk /dev/drbd0 to the folder /data as a file system ext3
mysqld -> This term is pointing to /etc/ha.d/resource.d/mysqld , it is a soft link to mysql startup script
httpd -> This term is pointing to /etc/ha.d/resource.d/httpd , it is a soft link to httpd startup script
Now let us make the soft links for mysqld and httpd init scripts under heartbeat resource folder as follows,
# cd /etc/ha.d/resource.d # ln -sf /etc/init.d/mysqld ./mysqld # ln -sf /etc/init.d/httpd ./httpd
Now we need to add the auth key /etc/ha.d/authkeys as follows,
auth 1 1 sha1 PutYourSuperSecretKeyHere
Make it little secure lol
# chmod 600 /etc/ha.d/authkeys
So our heartbeat installation completed.
Testing:
The DRBD is already running. Let us start hearbeat service in both servers.
# /etc/init.d/heartbeat start
You can monitor the log from /var/log/messages
Within one minute the HA IP will be available in your active server, also you can see the drbd partition /dev/drbd0 mounted to /data and mysql and httpd services are up and running.
Now stop the heartbeat server in active node and you can see the IP is activating in the passive server and it is starting the mysql and httpd services . Also the DRDB partition will be mounted in your passive server.
So now you can put what ever data to the folder /data, after mounting the partition /dev/drbd0 by the heartbeat. It will be replicated to other sever. This is a block replication method. So if you have a corrupted file in one server, it will be same in your other server too. So take care with your application.
Conclusion:
You can use the above active/passive high availability cluster for service like atmail , vbulletin , openx, etc,. It is also possible to move the mysql database to the DRBD partition too. But mysql master-master replication cluster is also good. Also make sure you may meed to connect the NIC with fast switches or cables , to move files faster.
I am not sure you will read this conclusion lol . If you do so , and you have any questions, please feel free to ask to me from the above contact page.
Categories
Subscribe Now
10,000 successful online businessmen like to have our content directly delivered to their inbox. Subscribe to our newsletter!Archive Calendar
| Sat | Sun | Mon | Tue | Wed | Thu | Fri |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
| 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 28 | ||||||
Recent Articles
-

Posted on : Jul 25
-

Posted on : Jul 07
-

Posted on : Apr 07
-

Posted on : Mar 19
Optimized my.cnf configuration for MySQL 8 (on cPanel/WHM servers)
Tags
- layer 7
- tweak
- kill
- process
- sql
- Knowledge
- vpn
- seo vpn
- wireguard
- webmail
- ddos mitigation
- attack
- ddos
- DMARC
- server load
- Development
- nginx
- php-fpm
- cheap vpn
- Hosting Security
- xampp
- Plesk
- cpulimit
- VPS Hosting
- smtp
- smtp relay
- exim
- Comparison
- cpu
- WHM
- mariadb
- encryption
- sysstat
- optimize
- Link Building
- apache
- centos
- Small Business
- VPS
- Error
- SSD Hosting
- Networking
- optimization
- DNS
- mysql
- ubuntu
- Linux